What is a VFD in HVAC System ?
Modern buildings bleed energy. HVAC systems alone consume nearly 40% of the power in commercial buildings. We see this waste every day in the field. The solution isn’t just “better equipment”—it’s smarter control. This is where the Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) transforms your HVAC infrastructure.
At OULU Electric, we don’t just manufacture drives; we engineer efficiency. Whether you run a chilled water pump or a massive air handling unit, understanding the VFD is your first step toward cutting operational costs.
VFD meaning in HVAC
You see the acronym everywhere. Let’s strip away the jargon.
1. VFD full form in HVAC
VFD stands for Variable Frequency Drive. In the HVAC world, you might also hear us call it a VSD (Variable Speed Drive) or an Inverter. They all refer to the same critical mission: controlling an electric motor by manipulating the power frequency supplied to it.
2. VFD stand for in HVAC
It stands for precision. A standard motor runs at one speed—full throttle. That is inefficient. A VFD acts as the nervous system, telling the motor exactly how fast to run based on real-time demand.
VFD function in HVAC
How does a VFD actually control a massive 50kW motor? It’s not magic; it’s power electronics.
1. VFD system in HVAC
Think of the VFD as part of a triad: The Controller (PLC/BMS), The VFD, and The Motor. In our EV510A Series, for example, the drive receives a command (like a 0-10V signal) from your building management system. It then processes this request using advanced current vector control algorithms to deliver precise torque and speed to the fan or pump.
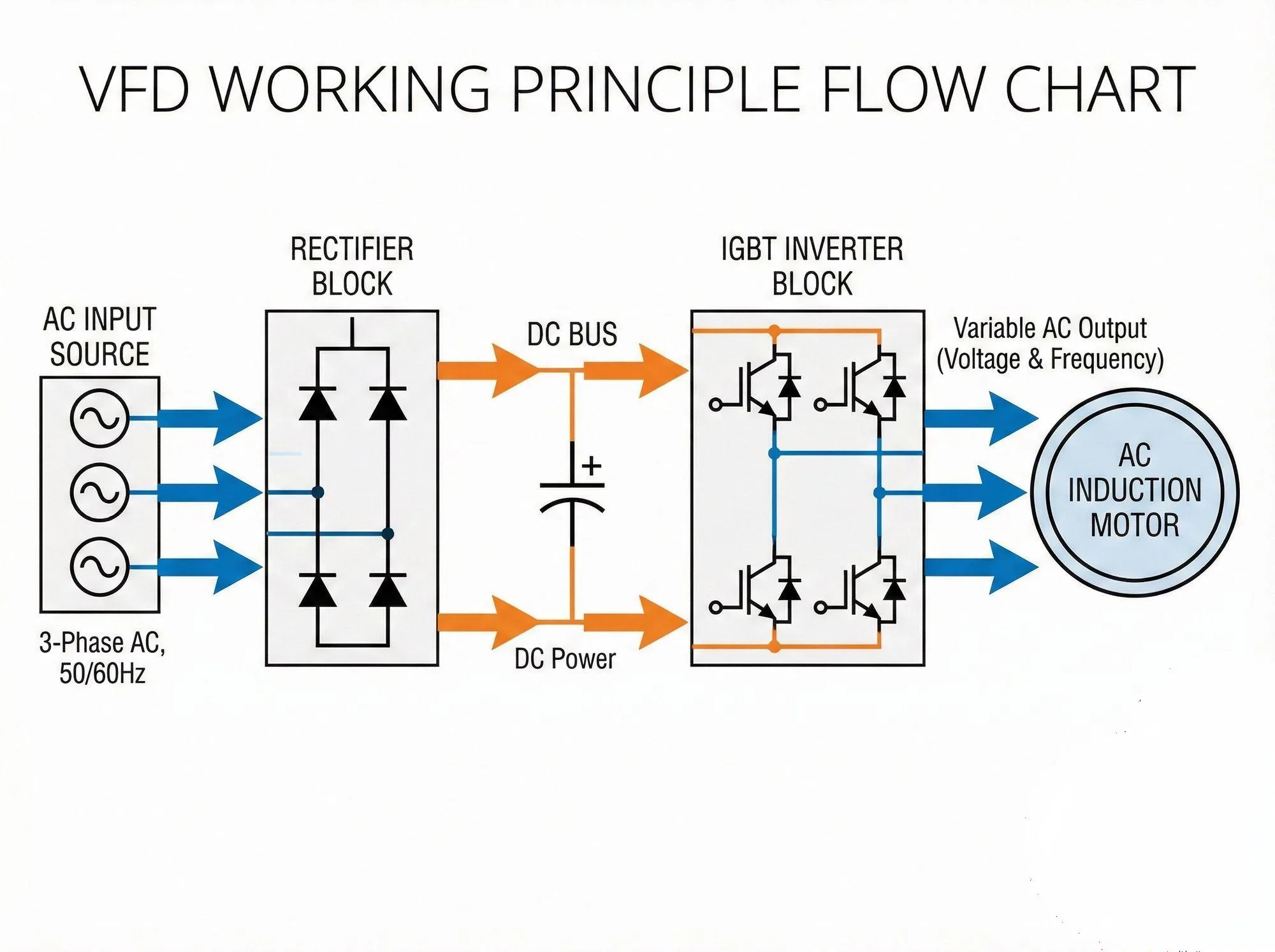
2. VFD working principle in HVAC
The process happens in three decisive steps:
- Rectification: We take the AC power from your grid (AC input L1/L2/L3) and smash it into DC power using a rectifier bridge.
- Filtering: Large capacitors smooth out this DC power, creating a stable “DC Bus.”
- Inversion: The brain of the VFD uses IGBTs (Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistors) to pulse this DC voltage back into AC. By changing how fast we pulse (Frequency), we dictate the motor’s speed (RPM).
Technical Insight: As noted in our EV200 Manual, a high-quality drive delivers high starting torque (0.5Hz can reach 150%) even at low speeds, ensuring your heavy fans start smoothly without jarring the belts.
The benefits of VFD in HVAC systems
Why install a VFD? The ROI speaks for itself.
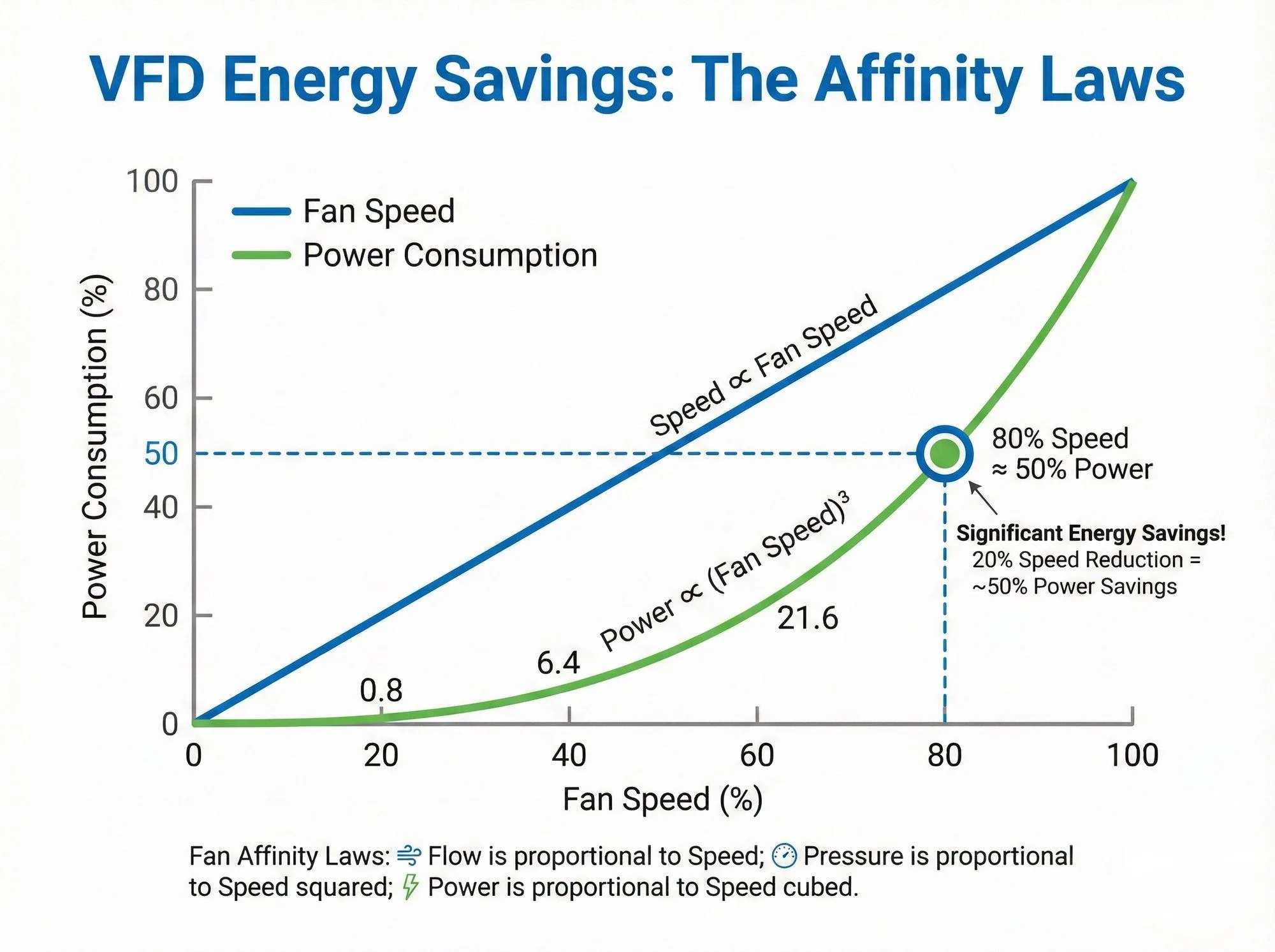
- Massive Energy Savings: This is non-negotiable. According to the Affinity Laws, reducing fan speed by just 20% cuts energy consumption by nearly 50%. We see these savings instantly when customers retrofit our EV210 series on older air handlers.
- Space & Cost Reduction: Real estate in a control cabinet is expensive. We designed the EV200 Series with a “narrow body” layout, reducing installation size by 30%. This allows independent air ducts and side-by-side mounting, slashing your distribution cabinet costs.
- Soft Starting: Direct-on-line starters hit your mechanical belts and couplings with a hammer blow of torque. VFDs ramp up speed gently. This extends equipment life and reduces maintenance downtime.
- Precise Process Control: With PID control functions built directly into drives like our EV210, the VFD maintains constant pressure in water supply pipes without needing external controllers.
Application of VFD in HVAC
We deploy VFDs across the entire mechanical room.
1.VFD applications in HVAC systems
- Air Handling Units (AHU): Regulating airflow based on CO2 levels or temperature.
- Cooling Tower Fans: Adjusting fan speed to maintain condenser water temperature.
- Boiler Feed Pumps: Managing water flow to match steam demand.
2.Use of VFD in HVAC
We specifically recommend using VFDs in variable torque loads (fans and centrifugal pumps). The energy savings here dwarf constant torque applications (like conveyors).
3.VFD used in HVAC
Retrofitting is a major market. You don’t need a new motor to get VFD benefits. Our drives work with standard asynchronous induction motors, breathing new life into aging HVAC infrastructure.
4.VFD in pumps
Water systems are where VFDs shine. In a Constant Pressure Water Supply scenario, the VFD reads a pressure sensor (4-20mA). If demand drops (someone closes a tap), the EV210 drive instantly slows the pump. If the feedback is lost, our drives trigger a “PID feedback lost” alarm (Fault code FU31), protecting your system from running dry.
5.Role of vfd in hvac chilled water system
Chilled water systems demand variable flow. The VFD modulates the chilled water pumps to match the cooling load of the building. This “Variable Primary Flow” design eliminates the need for energy-wasting throttling valves.

VFD panel in HVAC system
You rarely mount a VFD on a wall exposed. You house it in a panel.
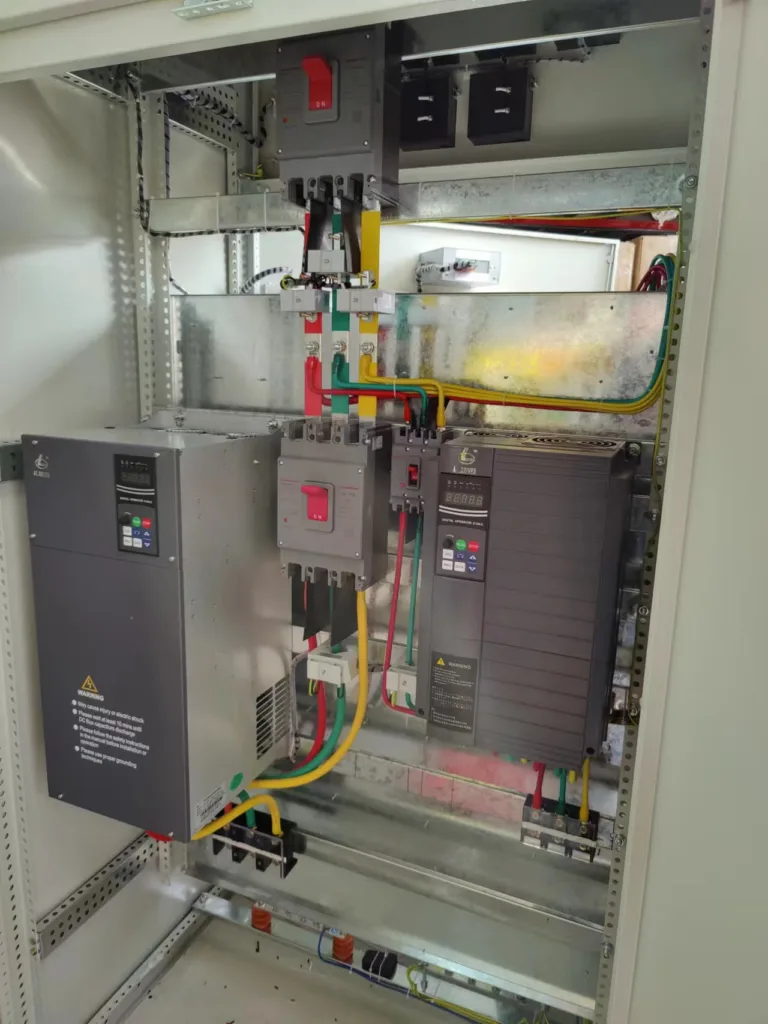

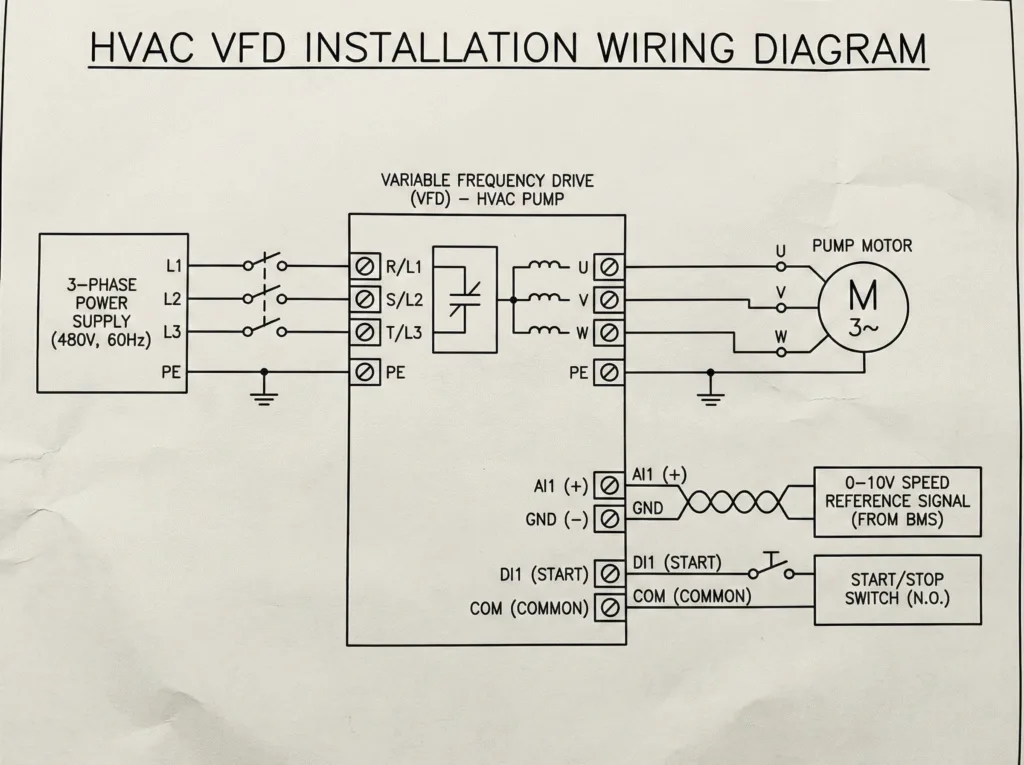
VFD HVAC wiring diagram
Proper wiring is the difference between a running system and a blown circuit. Referencing the Standard Wiring Diagram in our EV series manuals:
- Power Circuit: Connect 3-phase power to terminals R, S, T (or L1, L2, L3). Connect the motor to U, V, W. Never connect power to the output terminals—that destroys the drive instantly.
- Control Circuit: For HVAC, we usually wire a 0-10V signal to the Analog Input (AI) for speed reference and a dry contact to the Digital Input (DI/FWD) for the Start/Stop command.
Limitations of VFD in HVAC
We believe in transparency. VFDs are powerful, but they require engineering attention.
- Harmonics: VFDs introduce noise into the electrical grid.
- Environmental Limits: Electronics hate heat and dust. Our Selection Guide explicitly states: install indoors, free from direct sunlight, dust, and corrosive gas.
- Altitude Derating: If your facility is above 1000 meters, the thin air reduces cooling efficiency. You must derate the drive capacity—typically by 10% for every 1000m rise. Ignore this, and you will face overheating trips.
VFD HVAC Cost
Price is always a factor. However, compare the cost of a VFD to the cost of wasted energy. A standard starter is cheap. But a VFD, like our EV510A, often pays for itself within 12 to 18 months through energy savings alone. Plus, the reduction in mechanical wear adds years to your motor’s lifespan. That is smart money.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: what does vfd stand for in hvac?
A: Variable Frequency Drive. It controls motor speed by varying the frequency of the electrical supply.
Q: what is the function of a vfd in an hvac system?
A: It matches the motor’s output to the actual load requirement, saving energy and improving process control.
Q: what is a vfd in electrical?
A: It is a power conversion device that converts fixed-frequency AC power into variable-frequency AC power.
Q: what does an ac drive vfd do in hvac?
A: It allows AC induction motors, which normally run at a fixed speed, to run at variable speeds for fans and pumps.
Q: how vfd can save energy in hvac fan applications?
A: By following the Cubic Law: reducing fan speed by 10% reduces power consumption by roughly 27%.
Q: what is vfd in ahu?
A: It modulates the supply fan speed to maintain duct static pressure or building temperature without using mechanical dampers.
Conclusion
We don’t just sell boxes; we sell control. Integrating a Variable Frequency Drive into your HVAC system is the single most effective move you can make for energy efficiency. Whether you choose our compact EV200 for tight spaces or the robust EV210 for pump control, the technology is proven.
Stop wasting power. Start controlling it.