What is a VFD Drives?
VFD Drives (VFDs) as the core technical equipment in the field of industrial automation, has become the key equipment to improve energy efficiency and realize precise control. This article systematically explains the working principle, core advantages and selection points of VFD.
Variable Frequency Drive Definition and Full Name
VFD, known as Variable Frequency Drive, realizes motor speed regulation by changing the frequency of the power supply. Its technical nature is a power electronic conversion device, through the AC → DC → AC conversion process to generate adjustable frequency power supply. Alias includes: AC drive, variable frequency power supply, speed control drive, etc..
Working Principle Illustration
- Rectification: three-phase alternating current is converted to direct current by a diode rectifier bridge.
- DC link: capacitor bank smoothing voltage fluctuations, energy storage buffer
- Inverter: IGBT module generates pulse width modulation (PWM) waveforms.
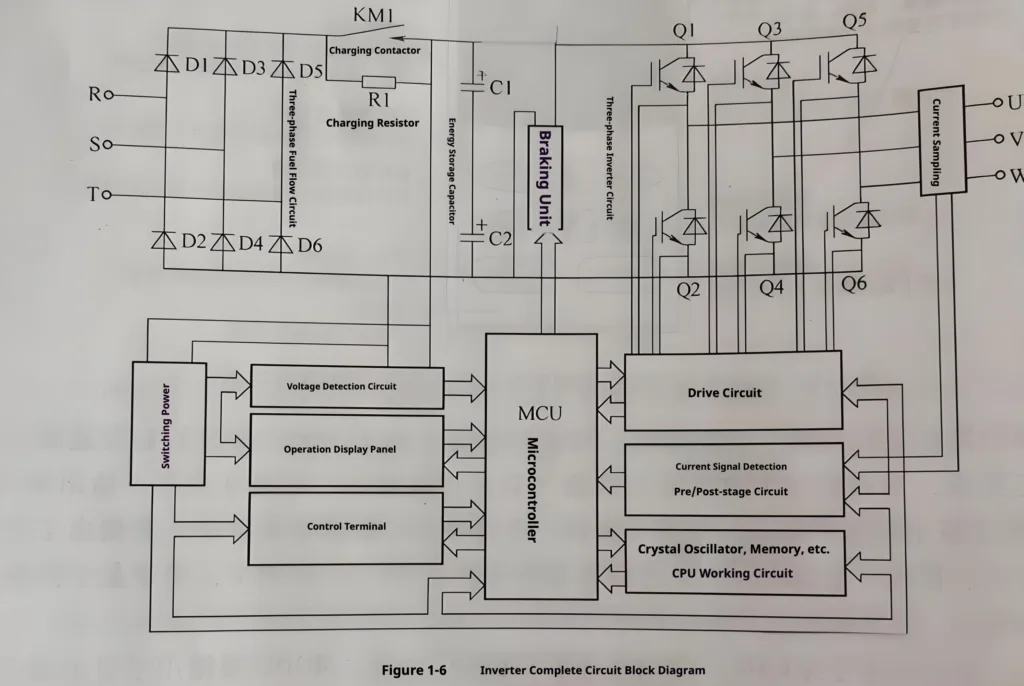
Core Components Explained
Module | Function Description |
|---|---|
Control Panel | Parameter setting and status monitoring interface |
Heat dissipation system | Forced air/liquid cooling system to maintain the component temperature <85℃. |
DSP controller | Realize vector operation and closed-loop control algorithm. |
IGBT module | Power semiconductor switching device, switching frequency up to 20kHz |
Core Advantage Comparison
- Energy Efficiency Improvement: 30%-60% energy savings for pump loads (NEMA data)
- Soft Start Protection: Limits starting current to 1.5 times the rated value.
- Extended life: Reduced mechanical shock increases bearing life by 2-3 times
- Dynamic Response: Vector control accuracy of ±0.2% speed error
Typical Applications & Recommended VFD Models
Application: Fan speed control for dynamic airflow adjustment
Key Requirements: Energy efficiency, harmonic mitigation
Recommended Models:
- Three Phase 90kW VFD Drives (Large commercial air handling units)
- Three Phase 185kW VFD Drives (Industrial ventilation systems)
Application: Constant-pressure water supply (±1% pressure stability)
Key Requirements: PID loop control, pump protection
Recommended Models:
- Three Phase 2.2kW VFD Drives (Residential booster pumps)
- Three Phase 5.5kW VFD Drives (Small-scale municipal stations)
Application: Conveyor belt synchronization
Key Requirements: Torque coordination, rapid I/O response
Recommended Models:
- Three Phase 15kW VFD Drives (Packaging line conveyors)
- Three Phase 18.5kW VFD Drives (Assembly line material handling)
Application: Floor-leveling control (±3mm accuracy)
Key Requirements: Sensorless vector control, brake management
Recommended Models:
- Three Phase 30kW VFD Drives (Mid-rise passenger elevators)
- Three Phase 45kW VFD Drives (High-speed commercial lifts)
Comparison with soft starters
Dimension | Inverter | Soft Starter |
|---|---|---|
Starting current | 100%-150% of rated current | 300%-500% of rated current |
Speed range | 0-100% continuously adjustable | Start-up phase control only |
Power factor | 0.98 (with PFC function) | 0.6-0.8 |
Typical Cost | $200/kW | $50/kW |
Installation and maintenance points
- EMC protection: power line and signal line spacing >200mm
- Grounding standards: PE grounding resistance <4Ω, wire diameter ≥ 50% of the phase line
- Heat dissipation requirements: installation spacing to maintain the upper and lower 50cm ventilation space
- Maintenance cycle: every 2,000 hours to check the capacitance capacity of the ash cleaning
HF Technology Q&A
Q: Will the inverter damage the motor?
A: Correct parameter settings can extend the life of the motor, but the wrong carrier frequency may lead to accelerated aging of the winding insulation.
Q: What is the principle of VFD energy saving?
A: By reducing the speed at partial load, the pump power demand decreases in proportion to the speed cube