What is VFD Overload? Causes, Wiring, and Solutions
Introduction
In the world of industrial automation, a tripping drive isn’t just a nuisance; it’s downtime. We see it constantly: a technician stares at a screen flashing “OL” or “FU40”, wondering if the drive is broken.
Here is the truth: A VFD overload is rarely a sign of a bad drive. It is a sign that your drive is doing exactly what we engineered it to do—protecting your motor and your facility from catastrophic failure.
At OULU Electric, we design our drives (like the EV200 and EV510A series) to handle tough industrial realities. But to fix an overload, you must stop guessing and start diagnosing. This guide explains exactly what causes VFD overload, how to wire for it, and how to solve it.
What is a vfd overload? Understanding the Basics
Many operators confuse “Overcurrent” with “Overload.” They are not the same.
A vfd overload is a thermal condition. It occurs when the current drawn by the motor exceeds the vfd overload rating for a specific period. It is an inverse-time relationship: the higher the current, the faster the drive trips.
Think of it this way:
- Overcurrent (Fault Code FU01 on EV200): A sudden, massive spike (like a short circuit). The drive trips in milliseconds.
- Overload (Fault Code FU40 on EV200): A gradual heat buildup. The motor draws 110% or 150% of its rated current. The drive calculates the heat accumulation (I²t) and trips before the motor insulation melts.
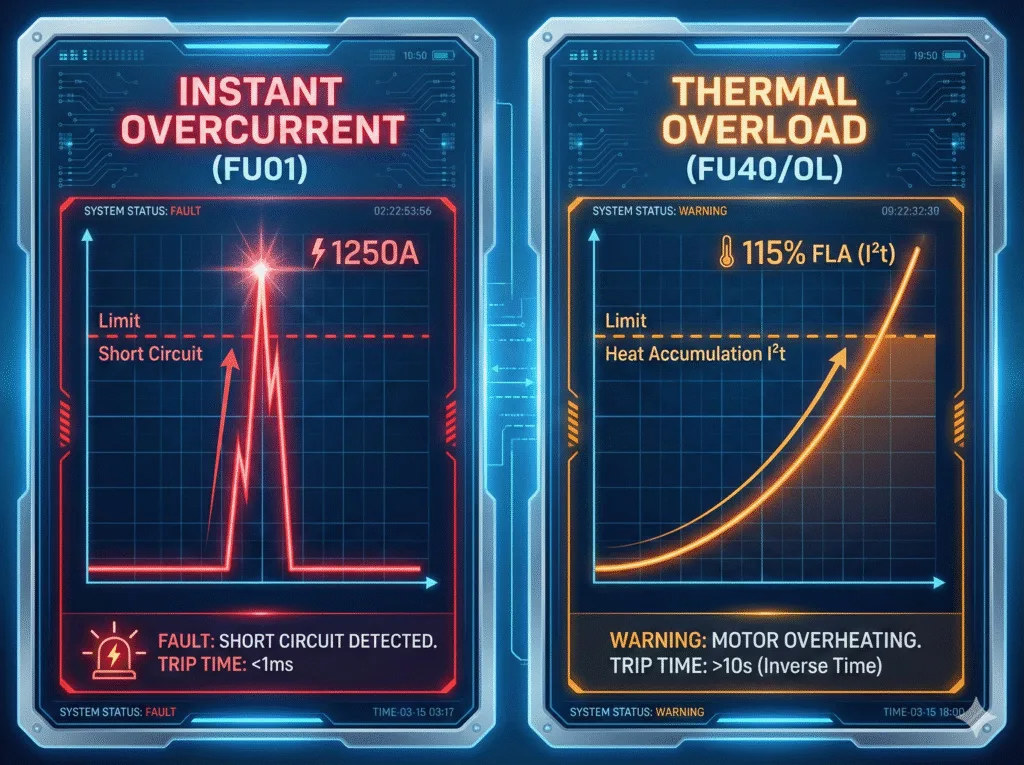
When you see a vfd drive overload, the drive is telling you: “I am working harder than you told me I should.”
Identifying the Main vfd overload fault causes
When your screen flashes an error, you need to know why. Based on our field experience and the EV200 User Manual, here are the primary culprits.
Why is my vfd tripping on overload?
If you encounter Fault Code FU40 (Motor Overload) or FU41 (Drive Overload), check these three physical realities immediately:
- Mechanical Jamming: Is the conveyor belt stuck? Is the pump bearing seized? A locked rotor forces the motor to draw maximum current, triggering the trip instantly.
- Excessive Load: You might be asking a 5kW motor to do a 7kW job.
- High Viscosity: In cold weather, oil or fluid becomes thicker. A pump that runs fine in summer might trip on vfd overload in winter because the viscosity increases the torque requirement.

Diagnosing a vfd overcurrent fault on startup
If the drive trips the moment you press “RUN,” you are likely not dealing with a thermal overload, but a short circuit or a ground fault. However, if the vfd overcurrent fault on startup happens after a few seconds of ramping up, your acceleration time might be too short.
- The Fix: Increase the acceleration time (Parameter P0-11 in EV200). Trying to spin a heavy fan from 0 to 50Hz in 1 second requires massive current. Give it 10 or 20 seconds.
Understanding the vfd inverter overload alarm Codes
On OULU drives, we separate the alarms to help you pinpoint the issue:
- FU40: Motor Overload. The calculation suggests the motor is overheating.
- FU41: VFD Module Overload. The drive’s own IGBTs are overheating.
Configuring vfd overload protection Parameters
You do not need external heaters or bi-metal strips. Modern OULU drives have sophisticated thermal models built into their software.
How to Adjust the vfd overload current setting
A common mistake we see is technicians leaving the drive at factory settings. You must set parameter P9-64 (Motor Rated Current) to match your motor’s nameplate.

If you have a 10A drive connected to a 5A motor, and you leave the setting at 10A, the drive will not protect the motor. It will happily let the motor burn up because it thinks the motor can handle 10A.
- Action: Look at the motor nameplate. Enter that Exact Amperage into the vfd overload current setting parameter.
Utilizing the Built-in electronic overload on vfd
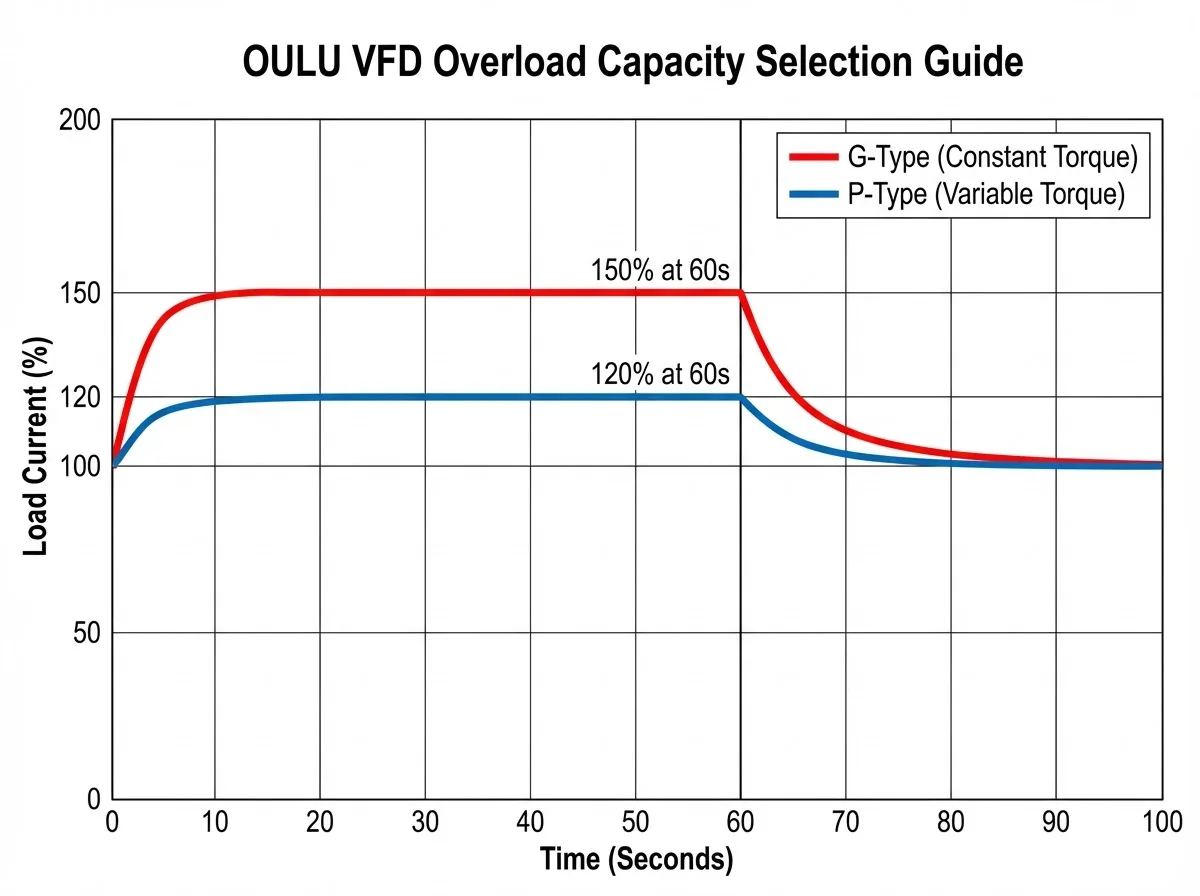
Our electronic overload on vfd function monitors the output current continuously. In the EV510A User Manual, this protection is standard. It integrates the current over time. If the current sits at 150% for 60 seconds (for G-Type loads), the drive trips. This internal calculation is far more accurate than a cheap mechanical relay because it accounts for the reduced cooling of a motor running at low speeds.
Correct Procedure for adjusting overload protection on vfd
- Enter Programming Mode.
- Navigate to Group P9 (Motor Parameters).
- Set P9-64 (Rated Current).
- Set P9-65 (Overload Pre-alarm): You can set this to 120%. This way, the drive gives you a warning signal before it actually trips, allowing your PLC to reduce the load automatically.
Guide to vfd drive wiring with overload relay
This is the most controversial topic in VFD installation. Do you need an external relay?
The Role of an External vfd overload relay
In 95% of single-motor applications, you do not need an external relay. The VFD handles it. However, if you are running multiple motors from one VFD (e.g., four small fans on one large drive), you MUST install an individual vfd overload relay for each motor. The VFD sees the total current and cannot detect if just one small motor is jammed.
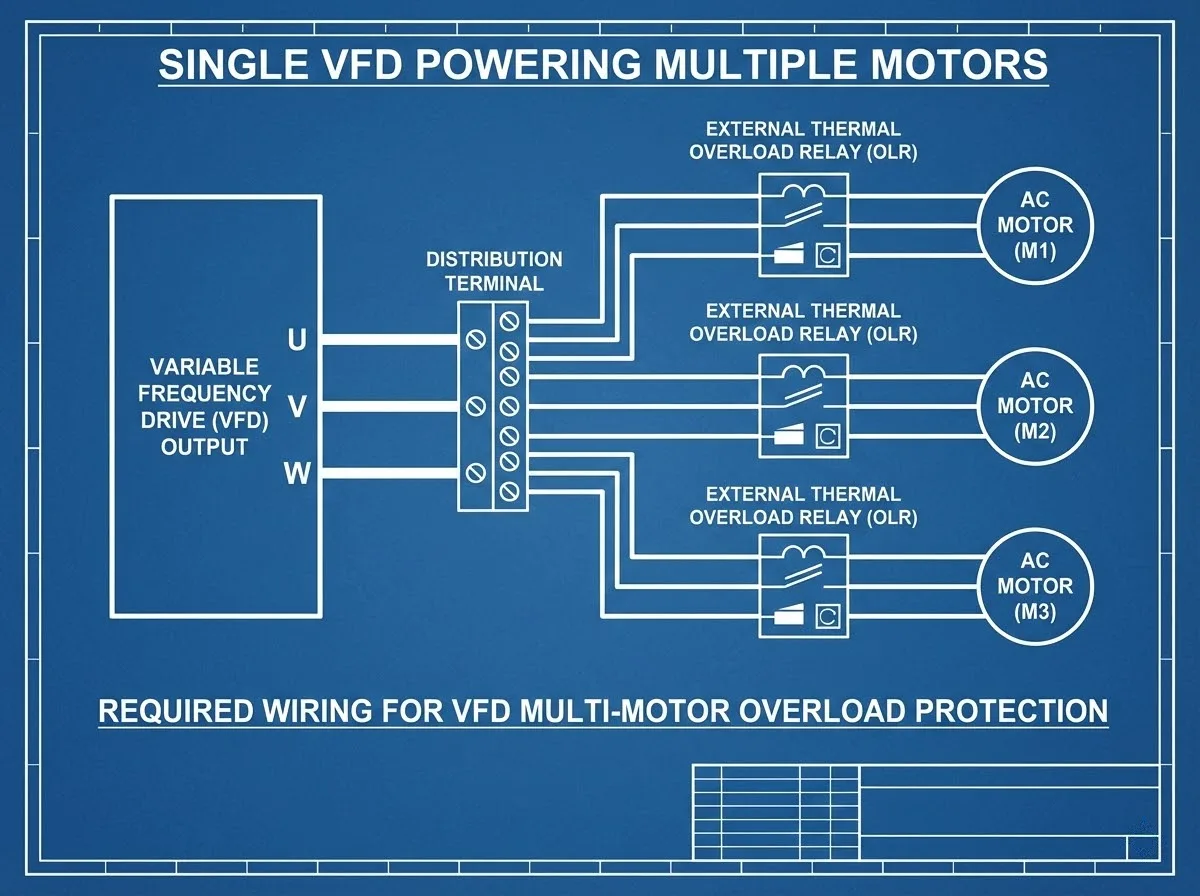
Should You Install an overload relay at the vfd input?
Absolutely not. Never put an overload relay at the vfd input. Input protection requires fast-acting fuses or a circuit breaker (MCCB) to protect against short circuits. An overload relay here is useless and introduces a point of failure.
Risks of Installing an overload after vfd
Installing a contactor or overload after vfd (on the output side) requires caution. If this relay opens while the VFD is outputting power, the sudden break in the inductive circuit causes a massive voltage spike. This spike can blow the VFD’s IGBTs.
- Our Rule: If you use an output relay, wire an interlock so the VFD stops before the relay opens.
Selection Guide: low overload vs high overload vfd
Not all drives are created equal. In our VFD Selection Guide, we categorize drives based on their vfd overload capacity.
When to Choose a high overload rated vfd
For “Constant Torque” loads like extruders, conveyors, and cranes, you need a G-Type (General) drive.
- Spec: 150% of rated current for 60 seconds.
- These loads need heavy torque to start and maintain speed.
When to Choose a low overload rated vfd
For “Variable Torque” loads like fans and centrifugal pumps, you can use a P-Type (Pump/Fan) drive.
- Spec: 120% of rated current for 60 seconds.
- Because water and air offer little resistance at low speeds, you do not need the extra heavy-duty capacity. Choosing a low overload rated vfd can often save you money on the unit size.
Step-by-Step vfd motor overload solution and Reset
The machine has stopped. The boss is watching. Here is your action plan.
How to Perform a vfd overload reset
- Check the Display: Confirm it is an Overload (OL/FU40) and not a Short Circuit (SC/FU01).
- Touch the Motor: Is it physically hot? If yes, let it cool. Resetting it immediately will just trip it again (the electronic overload on vfd has a thermal memory).
- Press RESET: On the OULU keypad, press the red STOP/RESET button.
- Check Current: As you restart, watch the Amps on the display. If it climbs instantly to the limit, you have a mechanical jam.
Preventing Future vfd motor overload fault Issues
- Clean the Motor: A motor covered in dust cannot cool itself.
- Check VFD Fans: If the FU41 (Drive Overload) triggers, ensure the VFD’s own cooling fans are spinning and the heat sink is clean.
- Verify Sizing: If you trip overload every day at 2:00 PM when production peaks, your drive and motor are simply undersized. Upgrade to a higher vfd overload rating.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What causes a VFD to overload?
A VFD overloads when the connected motor draws more current than the VFD’s rated capacity for a specific time. The three main causes are mechanical binding (jammed gears or bearings), undersized motor/drive for the application, or incorrect parameter settings (e.g., setting the motor rated current too low in the VFD).
What is overload capacity of VFD?
The overload capacity of VFD defines how much current the drive can handle above its continuous rating for a short burst.
- G-Type (Constant Torque): Typically handles 150% of rated current for 60 seconds.
- P-Type (Variable Torque): Typically handles 120% of rated current for 60 seconds. Refer to the OULU VFD Selection Guide for specific curves.
Do VFDs have overload protection?
Yes. All modern OULU drives feature built-in electronic thermal overload protection. This function calculates the motor’s temperature based on current and speed (I²t protection), eliminating the need for external mechanical overload relays in single-motor applications.
How to solve overload current?
- Identify the Load: Check if the machine is physically stuck or if the process load is too high.
- Check Parameters: Ensure parameter P9-64 (Motor Rated Current) matches the motor nameplate.
- Increase Accel Time: If it trips on start, increase the acceleration time (P0-11).
- Reduce Load: Slow down the process or reduce the mechanical resistance.
What are the three causes of overloading?
- Mechanical Issues: Seized bearings, blocked pumps, or jammed conveyors.
- Electrical Issues: Phase loss on the input/output or a short in the motor windings.
- Application Issues: Aggressive acceleration times or trying to drive a load heavier than the motor is rated for.
How to prevent overloading?
Prevent overloading by correctly sizing the VFD and motor for the application (High Overload vs. Low Overload). Keep the motor cooling fins clean, ensure the VFD’s internal fans are working, and set the vfd overload current setting accurately in the programming menu.
What type of overload would cause vfd to melt?
A standard overload will not cause a VFD to melt because the protection trips first. However, a short circuit (massive overcurrent) or a lightning strike can cause catastrophic failure where internal components melt or explode if the input fuses/breakers fail to clear the fault fast enough. Also, loose wiring connections can create high-resistance heat spots that melt terminals.
Did a vfd need an overload protection external?
No, not for a standard single-motor application. The VFD’s internal software is more accurate than an external bi-metal relay. You only need external vfd overload protection if you are powering multiple motors from a single VFD.
Does a vfd provide overload protection?
es. The VFD provides precise, adjustable overload protection. It monitors the output current and shuts down the output if the thermal limit is exceeded, protecting the motor insulation from burning out.
Should motor overload protection on output side of vfd drive?
Generally, no. You should rely on the VFD’s internal protection. If you must use an output contactor/overload for safety or multi-motor isolation, you must interlock it so the VFD is disabled before the switch opens. Opening a switch under load on the output side can damage the VFD’s transistors.
Conclusion
A vfd overload is a protection mechanism, not a disaster. It is your drive saving your hardware. By understanding the difference between high and low overload ratings, verifying your wiring, and trusting the internal protection of OULU drives, you ensure your production line runs smoother and safer.
Don’t bypass the protection. diagnose the root cause.